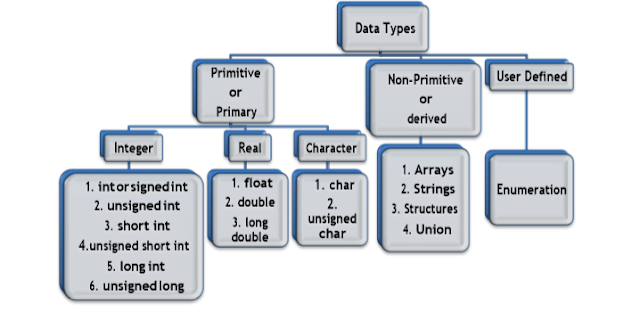
DATA TYPE:
1. Data type is used to specify what type of value to be stored in a
variable.
2. C language supports different types of data types.
3. The size and range of these data types may vary based on processor
type and compiler.
INTEGER DATA TYPES:
Integer
data types are used to represent value without decimal point. We can represent
signed values and unsigned values. In integer category we have int, short int,
long int as data types. The size and range of integer data types described in
below table.
TYPE SIZE RANGE
1.
short int 8 bits / 1 byte -128 to +127
2.
unsigned short int 8 bits / 1 byte 0 to 255
3.
Int 16 bits /2 bytes -32768 to +32767
4.
unsigned int 16 bits /2 bytes 0 to 65535
5.
long int 32 bits/4 bytes -2147483648 to +2147483647
6.
unsigned long int 32 bits/4 bytes 0 to 4294967295
1. In unsigned integer all bit positions are used to represent data.
2. In signed integer MSB bit is used to represent the sign (+,-) of a
value, remaining bits represent value.
REAL DATA TYPE:
These data types have at least one digit with a
decimal point. These are also signed and unsigned. Real data types are used to
represent a value in the form of MANTISSA and EXPONENT.
TYPE SIZE RANGE
`
1.
Float 32
bits / 4 bytes 3.4E-38
to 3.4E+38
2. Double
64 bits / 8
bytes 1.7E-308 to 1.7E+308
3. long double 80 bits
/ 10 bytes 3.4E-4932 to 1.1E+4932
1.
Float variables contains up to 6 digits of
precision where as double and long double have 10 digits of precision.
CHARACTER DATA TYPE:
By using character data type we can represent single
character or combination of characters called strings. Character data types are
either signed or unsigned.
TYPE SIZE RANGE
1. Char 8 bits /
1 byte -128
to +12 2. Unsigned char 8 bits / 1 byte 0 to 255
Magento Support Forum
ReplyDeleteWordPress Support Forum
I Like this information, Also suggest me other topics of this blog in reply, Keep Posting.
ReplyDeleteAlexa echo dot